Best Green Building Materials for Modern Eco Homes: Top Sustainable Picks
Building an eco home means cutting energy bills, improving indoor air quality, and reducing your environmental impact. Green materials help achieve this by sourcing responsibly, minimizing waste, and enhancing durability. Homeowners save up to 30% on utilities with proper insulation and efficient designs. These choices also boost property value—sustainable features appeal to buyers seeking healthier living spaces.
Start with basics. Green materials prioritize renewability, low embodied carbon, and recyclability. Bamboo grows rapidly, replacing itself in years, unlike hardwood that takes decades. Cork harvests without harming trees, offering natural insulation. Recycled steel cuts mining needs, while reclaimed wood repurposes old timber. Hempcrete blends hemp with lime for breathable walls that regulate humidity.
Benefits extend to health. Many avoid toxic chemicals found in conventional products, reducing allergens. In real builds, a California passive house used these to achieve net-zero energy, slashing costs. Another in the UK integrated them for superior thermal performance.
Challenges exist, like higher upfront prices, but long-term savings offset that. Availability varies by region—source locally to lower transport emissions. Certifications like FSC or Cradle to Cradle guide selections.
This guide highlights top options, with practical tips for integration. You’ll learn how to mix them for modern aesthetics without sacrificing function. Whether renovating or starting fresh, these materials transform homes into efficient sanctuaries.
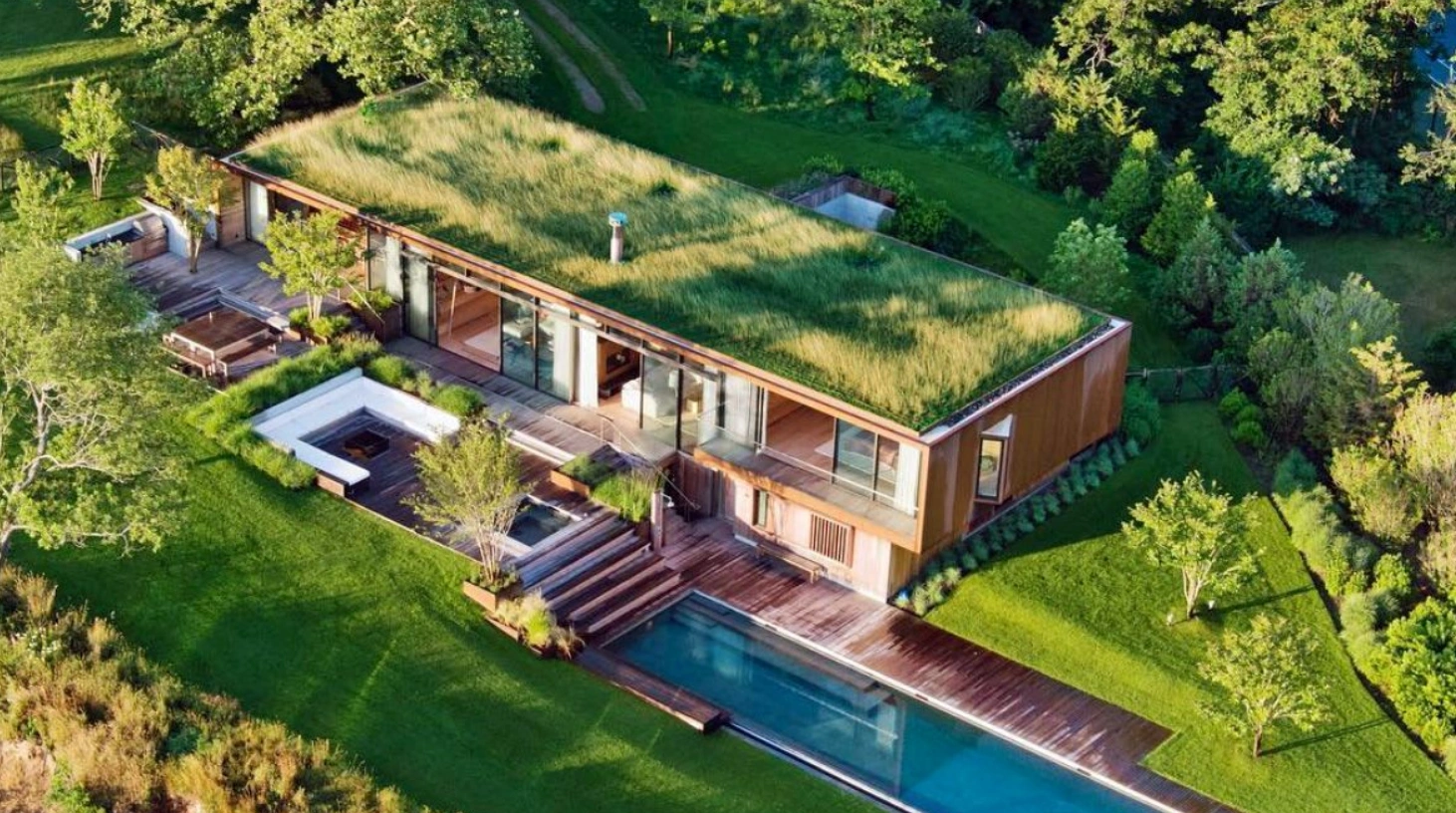

What Defines Green Building Materials?
Green building materials stand out for their low environmental footprint throughout their lifecycle—from extraction to disposal. They emphasize sustainability, like using rapidly renewable resources or recycled content to cut resource depletion. Embodied energy matters too; materials with low production emissions, such as those made locally, score high.
Key criteria include durability to reduce replacements, and non-toxicity for better indoor environments. For example, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in traditional paints harm air quality, but green alternatives skip them. Certifications help verify claims: Look for LEED or Energy Star ratings.
In practice, these materials integrate seamlessly into modern designs. A Seattle project used them to meet strict green codes, resulting in 40% less energy use. Tip: Assess total cost of ownership—initial spend versus lifelong savings on maintenance and bills.
Common misconceptions? They’re not always pricier long-term. Bulk sourcing or incentives offset costs. Plus, they enhance resale appeal in eco-conscious markets.
Overall, choosing green means balancing ecology with functionality. Research suppliers for transparency on sourcing.
Top Green Building Materials to Consider
Bamboo: Renewable and Strong
Bamboo excels as a structural and finishing material. It matures in 3-5 years, far quicker than trees, making it highly renewable. Used for flooring, walls, and beams, it rivals steel in strength-to-weight ratio.
In homes, engineered bamboo floors resist scratches better than some hardwoods. A Hawaiian residence framed entirely with it withstood high winds, proving resilience. Its natural antibacterial properties suit kitchens.
Tips: Treat for moisture resistance in wet climates. Source FSC-certified to ensure ethical harvesting. Costs run $3-7 per square foot for flooring.

Cork: Excellent for Insulation
Harvested from oak bark every nine years without tree damage, cork provides superb thermal and acoustic insulation. Ideal for flooring and underlayments, it cushions underfoot and dampens noise.
A Portuguese eco home used cork walls to maintain steady temperatures, cutting heating needs by 25%. It’s hypoallergenic and fire-resistant naturally.
Practical insight: Floating cork floors install easily over subfloors. Prices: $4-8 per square foot. Maintain with simple sealing.

Recycled Steel: Durable and Recyclable
Made from scrap, recycled steel frames homes with minimal new mining. It resists pests, fire, and earthquakes, lasting decades.
In an Australian build, it formed the skeleton, allowing open spans without extra supports. Recyclability hits 98%, closing the loop.
Tip: Galvanize for corrosion protection. Costs: Comparable to wood framing, around $2-4 per square foot.

Reclaimed Wood: Timeless Appeal
Salvaged from old structures, reclaimed wood reduces deforestation. Perfect for accents, beams, or siding, it adds character with unique grains.
A New York loft used barn wood for walls, blending rustic with modern. It sequesters carbon long-term.
Insight: Check for contaminants like lead paint. Prices vary: $5-15 per square foot.

Hempcrete: Breathable and Insulating
Mixed from hemp hurds and lime, hempcrete forms non-structural walls that regulate moisture and insulate effectively. Carbon-negative, it absorbs CO2 during growth.
A Canadian home used it for envelopes, achieving excellent energy efficiency. Mold-resistant, it’s ideal for humid regions.
Tip: Apply in panels; cures slowly. Costs: $10-15 per square foot.

Pros and Cons of Green Building Materials
- Pros:
- Lower long-term costs through energy savings and durability, often paying back in 5-10 years.
- Healthier indoors by avoiding toxins, reducing allergies in family homes.
- Environmental benefits like carbon sequestration, aiding climate goals.
- Aesthetic versatility for modern designs, from sleek to rustic.
- Cons:
- Higher initial investment, especially for rare materials like hempcrete.
- Availability issues in remote areas, increasing shipping emissions.
- Installation requires skilled labor familiar with eco techniques.
- Performance varies by climate; improper use leads to inefficiencies.
Alternatives to Green Materials
Standard concrete offers strength but high emissions. Pros: Widely available and cheap. Cons: Versus green options, it traps heat and lacks breathability, raising energy use.
Virgin timber provides natural looks. Pros: Easy to work with. Cons: Compared to reclaimed or bamboo, it depletes forests faster and needs more treatments.
Final Thoughts & Expert Insights
Green materials deliver efficient, healthy homes that align with sustainability. They cut impacts while enhancing comfort.
Recommendation: Prioritize based on needs—bamboo for structures, cork for interiors. Consult pros for integration. Start small with one material to test benefits.
FAQ
How do green materials affect home insurance rates? Many insurers offer discounts for sustainable features, lowering premiums by highlighting reduced risks like fire resistance.
Can green materials integrate with smart home tech? Yes, they complement sensors for better energy monitoring, optimizing efficiency in eco setups.
What maintenance differs for green versus traditional materials? Green options often need less, like natural sealing for cork, extending lifespan with minimal effort.
Do green materials limit design creativity? No, they enable innovative looks, from curved bamboo to textured hempcrete, expanding options.